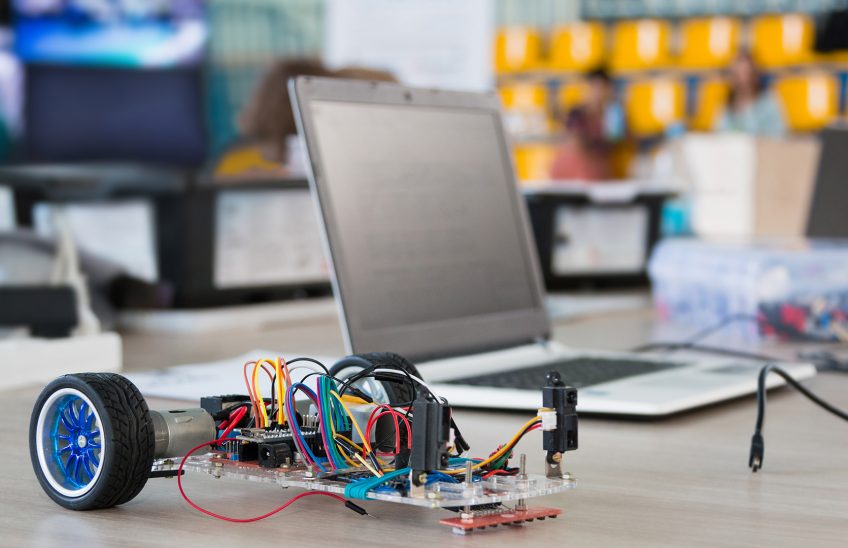
As an electronics design project, Munashe Matingo of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Stellenbosch University recently developed, tested and reported on a battery-powered remote-controlled car with collision avoidance. This forms part of a course presented by Professor Thinus Booysen, Prof CJ Fourier and Rita van der Walt.
This technology can be used for both recreational and commercial purposes, such as in autonomous vehicles or robotic systems. The use of this technology has become increasingly popular due to its ability to provide a safe driving experience while also reducing the risk of accidents.

How does it work?
The two wheels are propelled by DC motors, one with analogue electronics and sensing and the other with digital control and sensing. For proximity detection, ultrasonic sensors were used while torque commands were communicated by a remote control or cell phone.

In addition, WiFi connectivity was used to remotely relay telemetry, such as current through each wheel and battery characteristics, to a PC. A fascinating challenge I had to overcome was making the RC car move in a straight line considering the different controls of the wheels.
Practical use cases
Battery-powered remote-controlled cars with collision avoidance are becoming increasingly popular for a variety of use cases. For example, they can be used:
- in search and rescue operations to navigate hazardous terrain quickly
- as delivery vehicles to transport goods across difficult or dangerous terrain, such as in construction sites or warehouses.
These cars are also being explored for use in autonomous vehicle technology. They could potentially be equipped with sensors to help them navigate safely and efficiently on roads and highways by avoiding other vehicles and obstacles along the way. This is indeed a fascinating prospect for the future.
Final thoughts
Overall, a battery-powered remote-controlled car with collision avoidance is an example of the intersection between electrical and electronic engineering, robotics, and control systems. It combines advanced sensing, processing, and control technologies to create a smart, autonomous vehicle that can safely navigate its environment.